Sunday, 16 July 2017
Sunday, 7 May 2017
Wednesday, 26 April 2017
Hydraulic system
Hydraulic system : Mohammad
moklas
28.04.2017
A hydraulic driven drive framework is a drive or transmission
framework that utilizations pressurized pressure driven liquid to control water
powered hardware. The term hydrostatic alludes to the exchange of vitality from
stream and weight, not from the dynamic vitality of the stream.
Pressure driven machines are hardware and apparatuses that
utilization fluid liquid energy to do basic work. Substantial gear is a typical
case. In this kind of machine ,water driven liquid is transmitted all through
the machine to different pressure driven engines and water powered barrels and
progresses toward becoming pressurized by the resistance display.
these are the customary parts of repositories; new patterns
may introduce deviations from the standard. For instance, new plans for water
powered frameworks regularly call for stores that are considerably littler than
those in view of customary general guidelines. Since most frameworks warrant
some unique thought, it is essential to counsel industry models for least rules.
Hydraulic pump types
Fixed displacement types.
- Gear Pumps. Probably the simplest and most common used
today, they are easily maintained and economic. ...
- Gerotor Pumps.
- Screw Pumps.
Variable displacement types.
- Bent Axis hydraulic pumps.
- Axial Piston Pumps.
- Radial Piston Pumps.
Three main types of hydraulic pumps
are used in the fluid power industry. They are vane pumps, gear pumps and
piston pumps, all of which are types of positive
displacement pumps. Essentially, this means that they transfer a measured
quantity of pressurized hydraulic fluid into a hydraulic system.
Gear Pumps
Rigging are a kind of Rotary Positive
Displacement Pump. They comprise of no less than two discrete and turning gears
with intermeshing teeth. As these fit teeth discrete, they make an incomplete
vacuum which is filled by the liquid being pumped.
A rigging pump produces stream via
conveying liquid in the middle of the teeth of two lattice gears. One apparatus
is driven by the drive shaft and turns the idler rigging. The chambers framed
between nearby apparatus teeth are encased by the pump lodging and side plates
(likewise called wear or weight plates).
Gerotor
Gerotor is a positive relocation pump
The name gerotor is gotten from "Created Rotor". A gerotor unit
comprises of an inward and external rotor, with the external rotor having n+1
teeth with n characterized as a characteristic number more prominent than 2.
The hub of the internal rotor is counterbalanced from the pivot of the external
rotor and both rotors turn on their particular tomahawks. The geometry of the
two rotors segments the volume between them into n diverse powerfully evolving
volumes. Amid the get together's turn cycle, each of these volumes changes
constantly, so any given volume initially increments, and after that
abatements. An expansion makes a vacuum This vacuum makes suction, and thus,
this piece of the cycle is the place the admission is found. As a volume orders
pressure happens. Amid this pressure period, liquid can be pumped, or compacted
(in the event that they are vaporous liquids).
Gerotor pumps are for the most part
planned utilizing an inward rotor and an external rotor framed by a hover with
crossing roundabout arcs.
A gerotor can likewise work as a guns
High weight gas enters the admission zone and pushes against the internal and
external rotors, making both turn as the region between the inward and external
rotor increments. Amid the pressure time frame, the fumes is pumped out.
Screw Pumps.
Ascrew pump is a positive-displacement
(PD) pump that use one or several screws to move fluids or solids along the
screw(s) axis. In its simplest form (the Archimedes' screw pump), a single
screw rotates in a cylindrical cavity, thereby moving the material along the
screw's spindle.
Bent
Axis hydraulic pumps
Bent axis fixed displacement axial
piston pumps for open circuit applications are designed for operation in
systems typified by heavy duty work cycles. Closed circuit axial piston motors
are used mainly for rotary drives in power machinery or in hydrostatic
transmissions. Fixed displacement motors can also be used in open circuit applications,
and are therefore suitable for a variety of hydraulic circuits
Axial
Piston Pumps
A hub cylinder pump is a positive
uprooting pump that has various pistonsin a roundabout cluster inside a barrel
square. It can be utilized as a remain solitary pump, a water powered engine or
a car aerating and cooling compressor.
Radial Piston Pumps.
A spiral cylinder pump is a type of
water driven pump. The working cylinders stretch out in an outspread course
symmetrically around the drive shaft, rather than the pivotal cylinder pump.
Monday, 24 April 2017
Solenoid Valve Tutorial tips
Solenoid Valve Tutorial Tips: moklas
Solenoid valve definition:
A solenoid valve is an
electromechanically worked valve. The valve is controlled by an electric
current through a solenoid: on account of a two-port valve the stream is turned
on or off; on account of a three-port valve, the surge is exchanged between the
two outlet ports .A solenoid valve is an electromechanical controlled valve.
The valve includes a solenoid, which is an electric loop with a portable
ferromagnetic center in its middle. This center is known as the plunger. In rest
position, the plunger shuts off a little hole. An electric current through the
loop makes an attractive field. The attractive field applies a drive on the
plunger. Therefore, the plunger is pulled toward the focal point of the curl so
that the hole opens. This is the essential rule that is utilized to open and
close solenoid valves. "A solenoid valve is an electromechanical impelled
valve to control the stream of fluids and gases
Circuit
Functions Of Solenoid Valves
Solenoid
valves are utilized to close, measurements, disperse or blend the stream of gas
or fluid in a pipe. The particular reason for a solenoid valve is communicated
by its circuit work. A 2/2 way valve has two ports (delta and outlet) and two
positions (open or shut). A 2/2 way valve can be 'regularly shut' (shut in
de-invigorated state) or 'ordinarily open' (open in de-empowered state). A 3/2
way valve has three ports and two positions and can along these lines switch
between two circuits. 3/2 way valves can have distinctive capacities, for
example, regularly shut, typically open, redirecting or all inclusive. More
ports or mixes of valves in a solitary development are conceivable. The circuit
capacity can be communicated in an image. The following are a few cases of the
most well-known circuit capacities. The circuit capacity of a valve is
symbolized in two rectangular boxes for the de-empowered state (right side,
envisioned by ) and invigorated state (left). The bolts in the case demonstrate
the stream heading between the valve ports. The illustrations demonstrate a
2/2-way Normally Open (NO) valve, 2/2-way Normally Closed (NC) valve and a
3/2-way Normally Closed valve. For more data about valve images and circuit
capacities,
Direct Operated
Solenoid
valve have the most basic working standard. The medium moves through a little
opening which can be stopped by a plunger with an elastic gasket on the base. A
little spring holds the plunger down to close the valve. The plunger is made of
a ferromagnetic material. An electric loop is situated around the plunger. When
the loop is electrical empowered, an attractive field is made which pulls the
plunger up towards the focal point of the curl. This opens the hole so that the
medium can course through. This is known as a Normally Closed (NC) valve. A
Normally Open (NO) valve works the inverse way: it has an alternate development
so that the hole is open when the solenoid is not fueled. At the point when the
solenoid is impelled, the hole will be shut. The greatest working weight and
the stream rate are straightforwardly identified with the hole distance across
and the attractive drive of the solenoid valve. This standard is in this way
utilized for generally little stream rates. Coordinate worked solenoid valves
require no base working weight or weight contrast, so they can be utilized from
0 bar up to the greatest permissible weight. The showed solenoid valve is a
direct worked, typically shut 2/2 way valve.
Indirect
Operated (Servo Or Pilot Operated)
(additionally
called servo worked, or pilot worked) utilize the differential weight of the
medium over the valve ports to open and close. Generally these valves require a
base weight differential of around 0.5 bar. The channel and outlet are isolated
by an elastic film, likewise called stomach. The film has a little opening so
that the medium can stream to the upper compartment. The weight and supporting
spring over the layer will guarantee that the valve stays shut. The chamber
over the layer is associated by a little channel to the low weight port. This
association is hindered in the shut position by a solenoid. The breadth of this
"pilot" hole is bigger than the distance across of the gap in the
layer. At the point when the solenoid is stimulated, the pilot hole is opened,
which makes the weight over the layer drop. On account of the weight contrast
on both sides of the film, the layer will be lifted and the medium can spill
out of bay port to outlet port. The additional weight chamber over the layer
demonstrations like a speaker, so with a little solenoid still a huge stream
rate can be controlled. Aberrant solenoid valves can be utilized just for one
stream heading. Aberrant worked solenoid valves are utilized as a part of uses
with an adequate weight differential and a high coveted stream rate, such as
water system frameworks, showers or auto wash frameworks. Aberrant valves are
otherwise called servo controlled valves.
Semi-Direct Operated
Semi
coordinate worked join the properties of immediate and roundabout valves. This
enables them to work from zero bar, yet at the same time they can deal with a
high stream rate. They look to some degree like backhanded valves and
furthermore include a portable film with a little hole and weight chambers on
both sides. The distinction is that the solenoid plunger is straightforwardly
associated with the film. At the point when the plunger is lifted, it
specifically lifts the layer to open the valve. In the meantime, a moment hole
is opened by the plunger that has a marginally bigger measurement than the
primary hole in the layer. This causes the weight in the chamber over the film
to drop. Thus, the layer is lifted by the plunger, as well as by the weight
distinction. This mix brings about a valve that works from zero bar, and can
control generally expansive stream rates. Frequently, semi-coordinate worked
valves have more effective curls than backhanded worked valves. Semi-coordinate
worked valves are once in a while called helped lift solenoid valves.
Direct Operated 3/2 Way Solenoid Valves
A 3/2 way solenoid valve has three ports and two
exchanging states. In each exchanging state, two of the three ports are
associated. By initiating the solenoid, the valve switches state and an alternate
association between the valve ports is set up. The drawing beneath demonstrates
a direct worked 3/2 way valve. In the de-invigorated express, the medium can
stream between from the port on the correct side to the top port. In the
empowered express, the medium can spill out of the left port to the correct
port. This is a called a typically shut 3/2-way valve.
Sunday, 23 April 2017
Friday, 21 April 2017
Sensor Tips
Sensor
Tips moklas
Give us a chance to consider
an estimation framework. It is made out of an information gadget which detects the earth or
encompassing to create a yield and, a flag preparing square which forms the
flag from info gadget and a yield gadget which displays the flag to human or
machine administrator in a more clear and usable form.The beginning stage is info
gadget which is principally what we will talk about in this part.
A sensor is a gadget that reacts to any change in physical wonders or natural factors like warmth, weight, moistness, development and so on. This change influences the physical, synthetic or electromagnetic properties of the sensors which is additionally prepared to a more usable and coherent frame. Sensor is the heart of an estimation framework. It is the main component that interacts with ecological factors to create a
yield.
All sensors should be adjusted concerning some reference esteem or standard for precise estimation. The following is the figure of a thermocouple.Note that a transducer and a sensor are not the same. In the above given case of thermocouple. The thermocouple goes about as a transducer yet the extra circuits or segments required like the voltmeter, a show and so on together from a temperature sensor. Thus the transducer will simply change over the vitality starting with one shape then onto the next and all the rest of the work is finished by the extra circuits associated. This entire gadget shapes a sensor. Sensors and transducers are firmly identified with each other.
Qualities of Sensors
A
decent sensor ought to have the accompanying qualities
High
Sensitivity: Sensitivity shows how much the yield of the gadget changes with
unit change in info (amount to be measured). For instance the voltage of a
temperature sensor changes by 1mV for each 1oC change in temperature than the
affectability of the sensor is said to be 1mV/oC.
Linearity:
The yield ought to change straightly with the info.
High
Resolution: Resolution is the littlest change in the information that the
gadget can recognize.
Less
Noise and Disturbance.
Less
power utilization.
Sorts
of Sensors
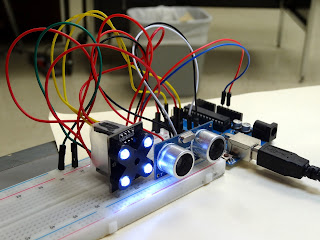
(1) Inductive sensor :Circuit diagram -

pressure tesduser sensor diagram:
Sensors are characterized in light of the way of amount they measure. Taking after are the sorts of sensors with couple of illustrations.
Sensor
characterization
In
view of the amount being measured
Resistance
temperature spoiler (RTD), a thermistor Thermocouple
Weight:
Bourdon tube, manometer, stomachs, weight gage
Constrain/torque:
strain gage stack cell
Speed/position:
Tachometer, encoder, LVDT
Light
Photo-diode light dependant resistor
Et
cetera.
Ulrasonics sensor circuit diagram:
Ulrasonics sensor circuit diagram:
(2) Active and detached sensors: Based on power prerequisite sensors can be delegated dynamic and aloof. Dynamic sensors are those which don't require outer power hotspot for their working. They create control inside themselves to work and henceforth called as self-producing sort. The vitality for working is gotten from the amount being measured. For instance precious stone create electrical yield (charge) when subjected to increasing speed. Detached sensors require outer power hotspot for their working. The vast majority of the resistive, inductive and capacitive sensors are inactive (similarly as resistors,inductos, and capacitor are called detached gadgets).
Microsonic sensor circuit diagram:
(3) Analog and computerized sensor: A simple sensor changes over the physical amount being measured to simple shape (ceaseless in time). Thermocouple, RTD, strain gage are called simple sensors. An advanced sensor produces yield as heartbeat. Encoders are case of advanced sensors.
(4)
Inverse sensors: There are a few sensors which are equipped for detecting a
physical amount to change over it to other shape and furthermore sense the
yield flag frame to get back the amount in unique frame. For instance a
piezoelectric precious stone when subjected to vibration creates voltage. In
the meantime when a piezo precious stone is subjected to differing voltage they
start to vibrate. This property make them appropriate to use in receiver and
speakers.
Monday, 17 April 2017
Lihgt
Ligght
Prologue TO HID LIGHTING HPS :
lighting
frameworks are one of a gathering of frameworks delegated High Intensity
Discharge lighting. The HID light gathering additionally incorporates all
mercury vapor and metal halide lighting frameworks. The HID light gathering is
one of the three noteworthy light gatherings utilized as a part of present day
lighting; the others are glowing and fluorescent. To better see how HID
lighting frameworks work, a short audit of brilliant and fluorescent light
operation is useful.
Brilliant Lamps / Incandescent Lamps:
A
regular tungsten glowing light has a tungsten fiber encased in a glass globule
loaded with idle gasses (Figure 1). At the point when electric current is gone
through the fiber, it offers imperviousness to the present stream. The fiber
warms up and shines, delivering light. As the light works, the tungsten fiber
vanishes and stores as dark fixes within the globule. The dormant gasses work
to decrease this darkening, yet can't dispense with it. Light yield lessens as
the fiber dissipates, and the light inevitably flops because of fiber breakage.
Tungsten incandescent lights attempt to diminish fiber vanishing by including
little measures of bromine, constraining the tungsten to redeposit on the
fiber. Incandescent light life is about twice that of ordinary glowing lights.
Glowing lights are accessible in wattages running from 2 to 1500 watts or more.
As a rule, the light level produced by a specific luminaire can be expanded or
diminished basically by changing to various light wattage.
Fluorescent Lamps :
Fluorescent
lights are low weight or Low Intensity Discharge lights. The light comprises of
a shut tube that contains two cathodes, a latent gas, for example, argon, and a
little measure of mercury (Figure 2). At the point when voltage is provided to
the light in the right sum, an electrical curve strikes between the two
cathodes. This circular segment transmits vitality that the phosphor covering
on the light tube changes over into usable light.
Shrouded Lamps / HID Lamps:
The
HID light gathering is by a long shot the most critical light gathering
utilized as a part of present day outside and mechanical lighting. Concealed
light sources are very respected for their long life and high viability. The
minimization of HID lights additionally increments optical control and takes
into consideration a lot of adaptability in the territory of luminaire plan.
Shrouded frameworks are the most financially savvy strategy for lighting
roadways, stopping territories, sports fields, signs and structures.Concealed
frameworks additionally are in a perfect world suited for inside applications,
for example, sports fields, distribution centers, mechanical plants and certain
sorts of roundabout office and business lighting
HID OPERATION AND CONSTRUCTION All HID
:
lights
share various plan and working elements, however there are some imperative
contrasts between mercury vapor, metal halide and HPS lights (Figure 3). All
HID lights contain a fixed circular segment tube mounted inside a glass knob.
In mercury vapor and metal halide lights, the globule is loaded with hydrogen
gas, which assimilates the bright radiation delivered amid operation. HPS
lights have a vacuum inside the globule to confine the circular segment tube
from changes in surrounding temperature. As the curve tube is fabricated,
little measures of uncommon circular segment metals, for example, mercury,
halide mixes or sodium, are fixed inside the tube. Beginning gasses, for
example, argon, neon or xenon, are set inside the tube. The curve tube
additionally houses the light's two principle cathodes, in addition to the
different beginning terminal utilized as a part of mercury vapor and metal
halide lights. A HID light creates light in much an indistinguishable way from
a lightning jolt. In any case, rather than a concise glimmer, the electric
curve between the light's two principle terminals is nonstop. The striking and
keeping up of this ceaseless bend is made conceivable by the beginning gasses
and circular segment metals fixed inside the curve tube. The best possible
start-up voltage additionally is expected to build up the bend. Light start-up
is not the same for all HID